New Targeted Therapy for Colorectal Cancer
The FDA has approved another inhibitor of the VEGF receptor family for patients with metastatic, heavily pretreated colorectal cancer.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved fruquintinib (Fruzaqla) for adult patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) that has been previously treated with a VEGF-targeted therapy; a chemotherapy regimen consisting of fluoropyrimidine, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan (FOXIRI); and, if the patient is eligible, a therapy targeting EGFR.
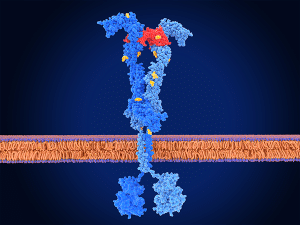
Fruquintinib is a type of targeted therapy called a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. It binds to a family of tyrosine kinases called VEGF receptors and prevents them from sending signals that promote tumor cell proliferation. VEGF receptor blockade also hinders the growth of new blood vessels that bring essential oxygen and nutrients to the tumor. This is the first FDA approval for fruquintinib.
The approval was based on results from two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III clinical trials: FRESCO, which was performed in China, and FRESCO-2, which was performed internationally. In both trials, patients were randomly assigned 2:1 to receive fruquintinib or placebo until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. FRESCO included 416 patients with mCRC who had previously received FOXIRI, and FRESCO-2 included 691 patients who had previously received FOXIRI, an anti-VEGF therapy, additional chemotherapeutics, and, if eligible, anti-EGFR therapy.
In FRESCO, the median overall survival was 9.3 months among patients in the fruquintinib arm and 6.6 months among patients in the placebo arm. In FRESCO-2, patients in the fruquintinib arm had a median overall survival of 7.4 months, and patients in the placebo arm had an overall survival of 4.8 months.
Colorectal cancer is a cancer of the tissues that make up the large intestine. According to federal statistics, it was estimated that 153,020 individuals would be diagnosed with colorectal cancer and 52,550 patients would die of the disease in the United States in 2023.
The FDA rendered its decision on November 8, 2023.
